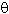 =
= 
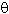 of an adsorbate on a surface is generally defined as follows:
of an adsorbate on a surface is generally defined as follows:
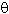 =
= 
The total number of adsorption sites is often equal to the total number of surface atoms
of the substrate.
A monolayer is defined as the coverage for which 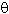 =1.
=1.
For large molecules (such as the fullerene family we'll discuss in Section 8) a monolayer may also be defined as the coverage that results in a close packed, single molecule thick layer.