About Natural Sciences

Natural Sciences students are taught by scientists across nine schools who are working towards solutions to today’s global problems.
Natural Sciences has been designed as a flexible, tailored degree that aligns with your academic interests and career goals and enables you to pursue your chosen disciplines to an advanced level. You'll benefit from research-led teaching on a programme accredited by the Society for Natural Sciences as offering outstanding interdisciplinary education.
You begin studying three subjects in your first year from 22 available combinations that we call streams and gradually specialise over the course of your degree. Subjects available on Natural Sciences are:
| Archaeology |
Earth Science |
| Biology |
Ecosystems & Environment |
| Cancer Sciences |
Mathematics |
| Chemistry |
Physics |
| Computer Science (intercalated year) |
Psychology
|
How does the course work?
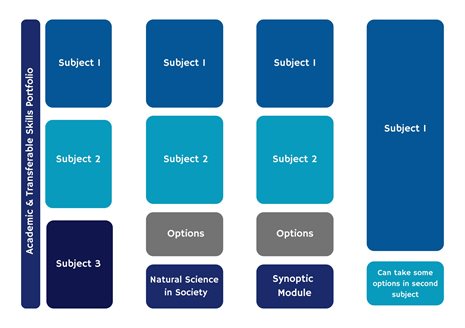
Natural Sciences offers you the opportunity to study three subjects within a single, multidisciplinary degree. In your first year, you’ll study all three subjects, before narrowing down to two in your second year to build deeper expertise.
Each year, you'll take 40 credits from each of your core subjects, developing both theoretical understanding and practical skills. You’ll study alongside students on single-subject degrees, ensuring the same academic depth, while benefiting from a broader, disciplinary perspective.
In addition to your subject blocks, a 20-credit optional block in years two and three allows you to tailor your studies to your interests and future plans. Some options are prerequisites for later modules or research projects, while others offer flexibility to explore new areas, including a third subject.
From first to third year, Natural Sciences-specific modules support your development as an interdisciplinary scientist. These modules help build a strong cohort identity and foster your ability to connect ideas across scientific disciplines. In Year 1, you’ll focus on essential skills for succeeding as a science student. In Year 2, Science and Society: Data and Bias explores who participates in science, who is excluded, and how science is communicated, enhancing your data analysis, critical thinking, and societal awareness.
A highlight of the course is the Year 3 synoptic project, a collaborative group project with students from other streams. You'll contribute your subject expertise and apply your learning in new, integrative ways.
If you pursue the MSci pathway, your fourth year focuses on a major research project, usually within one discipline but sometimes spanning multiple areas. You’ll also select advanced optional modules from one or both of your third-year subjects.
Available Streams
- Archaeology-Biology-Chemistry
- Archaeology-Biology-Earth Science
- Archaeology-Earth Science-Chemistry
- Biology-Chemistry-Maths
- Biology-Physics-Maths
- Cancer Sciences-Biology-Chemistry
- Cancer Sciences-Biology-Psychology
- Chemistry-Archaeology-Ecosystems & Environment
- Chemistry-Physics-Maths
- Ecosystems & Environment-Biology-Archaeology
- Ecosystems & Environment-Biology-Chemistry
- Ecosystems & Environment-Earth Science-Archaeology
- Earth Science-Biology-Chemistry
- Earth Science-Ecosystems & Environment-Biology
- Earth Science-Ecosystems & Environment-Chemistry
- Maths-Earth Science-Biology
- Maths-Earth Science-Chemistry
- Maths-Psychology-Chemistry
- Physics-Earth Science-Maths
- Physics-Psychology-Maths
- Psychology-Biology-Chemistry
- Psychology-Biology-Maths
Natural Sciences Programmes available:
Programmes which are not available to apply to directly are transferred to during your second year.