Cardiology Teaching Package
A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
The Heart
The heart itself is made up of 4 chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles. De-oxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart via the venous circulation. It is pumped into the right ventricle and then to the lungs where carbon dioxide is released and oxygen is absorbed. The oxygenated blood then travels back to the left side of the heart into the left atria, then into the left ventricle from where it is pumped into the aorta and arterial circulation.
Image: The passage of blood through the heart
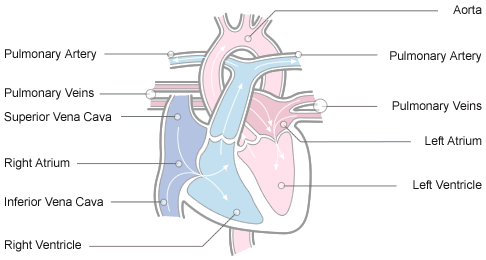
The pressure created in the arteries by the contraction of the left ventricle is the systolic blood pressure. Once the left ventricle has fully contracted it begins to relax and refill with blood from the left atria. The pressure in the arteries falls whilst the ventricle refills. This is the diastolic blood pressure.
The atrio-ventricular septum completely separates the 2 sides of the heart. Unless there is a septal defect, the 2 sides of the heart never directly communicate. Blood travels from right side to left side via the lungs only. However the chambers themselves work together . The 2 atria contract simultaneously, and the 2 ventricles contract simultaneously.
So what we need to know next is "what causes these chambers to contract?".
