Open Source Software & Data
Access software tools produced by our researchers.
- HistoryMap/SenseMap: an interactive tool to support online research
PrompTHis: an interactive tool support (artists) using generative image models (diffusion models)
- Vitality 2: an LLM-based interactive literature research tool
MoneyVis: Open Bank Transaction Data for Visualization and Beyond
2D/3D Interactive Medical Image Segmentation
Project Summary: Image segmentation is a crucial step in many medical image analysis processes. Manual or semi-automatic image segmentation is often necessary to provide accurate annotations for supervised machine learning algorithms or to be directly used for clinical feature quantification. Our software aims to enable rapid interactive image segmentation for both 2D and 3D medical images based on full-connected conditional random field method. It supports up to 10 foreground labels and various image format (Matlab, Nifty, DICOM, etc.). The software was developed in Matlab, hence the Matlab runtime library will be automatically installed. Please make sure you have internet connections during the installation process. The software is freely available for research purposes, please cite our paper if it is useful to your project.
Team Members: Ruizhe Li and Xin Chen
Open Source Code URL: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JIzWkT3M-X7jeB8tTwVcEw240TGbJAvj/view
References: Ruizhe Li and Xin Chen, An efficient interactive multi-label segmentation tool for 2D and 3D medical images using fully connected conditional random field, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, vol 213, 2022, doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106534
The project proposes a new multimodal dataset seqGraph, comprising semantic, image and audio representations of diatonic harmonic sequences (in C major only). The dataset was tested in a generative setting with a custom spiking convLSTM model and shown the best results compared to the models trained with the seqMNIST (custom selection of the MNIST images to form the sequences of digits) and MovingMNIST. The current stage of the experiment involves the exploitation of the visual data, received out of the sequences of chords represented via the system of graphs. The additional dimension introduced via graph representation allowed 2D representation of the initial 1D data and the application of the image data augmentation strategies.
Link to page - SeqGraph
This repository presents a bilingual English–French dataset and benchmark with parallel data ConceptFR for constrained text generation task. The dataset contains 28K of English–French sentence pairs with the keywords and a main concept for each data entry. This dataset targets testing the generative abilities of a model to produce a commonsense knowledge text given a set of keywords as a condition. The article[1], which describes the experiment results, was published in the ACM Digital Library.
Link to page - ConceptFR
- Bias filters as part of the NL-Augmenter toolkit for NLP (2023)
Pipelines for data cleaning, generative model fine-tuning, and evaluation for the ConceptFR bilingual dataset (2024)
A repository containing the project files for ConceptFR, aimed at constraint text generation.
Link to page - GitHub - asnota/conceptfr
Spiking ConvLSTM model implementation with seqGraph dataset resources (2023)
A repository for the code of the experiment described in the article "Spiking ConvLSTM for Semantic Music Generation."
Link to page - GitHub - asnota/spiking_convlstms
Cardographer web platform
Cardographer is a web platform for creating, using and analysing pre-defined concept cards, e.g. ideation cards. It was developed at the University of Nottingham and supported by the UKRI-funded Horizon projects [Grant Numbers EP/T022493/1 and EP/V00784X/1]. Once a card deck has been created or imported into Cardographer the cards can be accessed in a simple phone-friendly web view (e.g. the Responsible Innovation Prompts & Practice cards,https://cardographer.cs.nott.ac.uk/sessions/64be3ee7f2068c32233f71f2/cards). A Cardographer session can be linked to a Miro online whiteboard, making it easy to add cards to the Miro board and providing extra functions via the Cardographer web view such as spotlighting cards, individual hands and card dealing. The Cardographer Miro plugin also allows card use information to be saved and analysed later in Cardographer.
There is a public demonstration instance of Cardographer hosted by the University at https://cardographer.cs.nott.ac.uk/ but for significant use it is best to deploy your own instance. The user guide is in the github Wiki, https://github.com/MixedRealityLab/cardographer-platform/wiki
Link to page - https://github.com/MixedRealityLab/cardographer-platform/
Development team: Chris Greenhalgh, Kevin Glover, Edgar Bodiaj.
The Brain Data Group Projects
BenchNIRS
BenchNIRS is an open source Benchmarking framework for machine learning with fNIRS. This benchmarking tool makes sure that all comparisons of approaches to classification using different approaches to machine learning of fNRIS data are suitably comparable, and not affected by poor methodological choices often found in papers.
Link to page - https://gitlab.com/HanBnrd/benchnirs
NIRSync
NIRSync is a free tool to sync up video data with fnirs data collection, to then add additional labels to the data for a) noise, and b) any missed trigger points in the task setup. The tool reads in SNIRF and video files, provides the ability to line up data and video, and then watch them both playback in parallel. The tool exports SNIRF with extra labels added.
Link to page - https://gitlab.com/brain-data-uon/nirsync
Mobile Phone Extraction (MPE)
Mobile Phone Extraction (MPE) is a process in which the police download content from a mobile phone belonging to a suspect, witness or victim in a crime to aid their investigations. Whilst, this process can significantly benefit criminal justice outcomes, it also raises concerns over intrusion of privacy and inefficiency due to the large amounts of personal data collected and the extensive amount of time required to analyse it.
RIME (Responsible Investigation of Mobile Environments) is an open-source tool for MPE. It was developed as part of two research projects, both funded by the UKRI Trustworthy Autonomous Systems Hub: ‘Digital Forensics Platform’, and ‘Trustworthy and Useful Tools for Mobile Phone Extraction’ . RIME is designed to expose a subset of mobile phone data, rather than the full dataset, for investigation. It also includes pseudonymisation features. Through the development of RIME our projects explored opportunities to enhance the usefulness and trustworthiness of MPE tools – for instance by identifying optimum mechanisms for data search and filtering, results visualisations, and privacy protection. RIME is available at rhttps://github.com/horizon-institute and you can access a demo video here https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yWPtZabWyCg
Project Title: NottReal - A Tool for Voice-based Wizard of Oz studies
Team Members: Martin Porcheron, Joel Fischer, Michel Valstar
Open Source Code URL: https://github.com/MixedRealityLab/nottreal/
Programming Language: Python
Type of Software License: MIT License
Project Summary: NottReal is an interactive tool to support Wizard of Oz studies by simulating a Voice User Interface, including both optional audio and visual output. Its main features include: 1) tabbed lists of pre-scripted messages, 2) entry for custom messages, 3) currently queued messages, 4) previously sent messages, 5) previously filled slots, and 6) options to log events and send messages with a loading animation (see Figure 1).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3405755.3406168
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments: This work was supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council [grant number EP/N014243/1] and the Department for International Development.
Project Title: DECSYS – Discrete and Ellipse-based response Capture SYStem
Team Members: Zack Ellerby, Josie McCulloch, John Young, Christian Wagner, Oliver Miles
Open Source Code URL: https://github.com/decsys/decsys
Type of Software License: AGPL-3.0-only
Project Summary:
DECSYS is a newly developed open-source software tool, which enables the creation and administration of digital surveys that elicit both conventional and interval-valued responses. DECSYS incorporates a range of features, and is designed to maximise versatility for experimenters and usability for participants. Surveys can be conducted either locally or online, and results easily exported.
References:
C. Wagner, S. Miller, J. M. Garibaldi, D. T. Anderson and T. C. Havens, "From Interval-Valued Data to General Type-2 Fuzzy Sets," in IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 248-269, April 2015, doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2310734.
Z. Ellerby, J. McCulloch, J. Young and C. Wagner, "DECSYS – Discrete and Ellipse-based response Capture SYStem," 2019 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2019, pp. 1-6. DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2019.8858996
Z. Ellerby, O. Miles, J. McCulloch and C. Wagner, "Insights from interval-valued ratings of consumer products—a DECSYS appraisal," 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2020, pp. 1-8. DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ48607.2020.9177634
Z. Ellerby, C. Wagner, S. Broomell, “Capturing Richer Information—On Establishing the Validity of an Interval-Valued Survey Response Mode”, Accepted to Behavior Research Methods, 2021.
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments (optional): The development of the software has been supported in part by the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) and the UK EPSRC grant EP/P011918/1: Leveraging the Multi-Stakeholder Nature of Cyber Security
Project Title: SyFSeL (Synthetic Fuzzy Set Library)
Team Members: Josie McCulloch
Open Source Code URL: https://bitbucket.org/JosieMcCulloch/syfsel/src/master/
Programming Language: Python
Type of Software License: GPL-3
Project Summary:
SyFSeL is a free open-source library that automatically generates synthetic fuzzy sets aimed to for use in empirically testing methods developed for fuzzy sets. SyFSeL generates as many sets as desired, with specified membership function type (normal, bi-modal or multi-modal) and fuzzy set type (type-1 or type-2) to enable users to emulate real data. Fuzzy sets are stored in csv format so users can easily import the generated sets into their own fuzzy systems software and SyFSeL can also create graphical plots of the generated sets.
References: J. McCulloch, "SyFSeL: Generating Synthetic Fuzzy Sets Made Simple," 2018 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2018, pp. 1-6.
DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2018.8491549
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments (optional): The development of the software has been supported in part by the UK EPSRC grant EP/P011918/1: Leveraging the Multi-Stakeholder Nature of Cyber Security
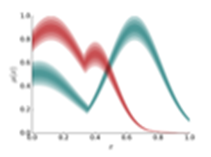
Project Title: Fuzzycreator
A python-based toolkit for automatically generating and analysing data-driven fuzzy sets
Team Members: Josie McCulloch
Open Source Code URL: https://bitbucket.org/JosieMcCulloch/fuzzycreator/src/master/
Programming Language: Python
Type of Software License (optional): GPL-3
Project Summary:
fuzzycreator is a free, open-source, python based toolkit that facilitates the automatic generation of type-1 and type-2 fuzzy sets from data, and their analysis through measures such as similarity and distance.
References: J. McCulloch, "Fuzzycreator: A python-based toolkit for automatically generating and analysing data-driven fuzzy sets," 2017 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2017, pp. 1-6.
DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2017.8015445
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments (optional): The development of the software has been supported in part by the UK EPSRC grant EP/P011918/1: Leveraging the Multi-Stakeholder Nature of Cyber Security
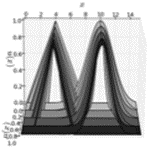
Project Title: Juzzy - A Java based toolkit for Type-2 Fuzzy Logic
Team Members: Christian Wagner
Open Source Code URL: http://juzzy.wagnerweb.net/
Programming Language:Java
Type of Software License: BSD-3
Project Summary:
Juzzy is a free, open-source, Java based library for the design and implementation of type-1, interval and general type-2 set and system based applications.
References: C. Wagner, "Juzzy - A Java based toolkit for Type-2 Fuzzy Logic," 2013 IEEE Symposium on Advances in Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Systems (T2FUZZ), 2013, pp. 45-52
DOI: 10.1109/T2FZZ.2013.6613298.
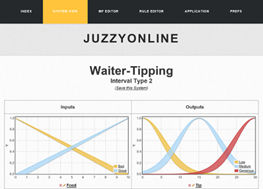
Project Title: JuzzyOnline
An online toolkit for the design, implementation, execution and sharing of Type-1 and Type-2 fuzzy logic systems
Team Members: Christian Wagner
Open Source Code URL: http://juzzy.wagnerweb.net/
Programming Language: Java
Project Summary:
JuzzyOnline is a browser-based toolkit for the design and execution of type-1, interval and general type-2 fuzzy logic systems. JuzzyOnline includes features for generating figures for all types of fuzzy sets.
References: C. Wagner, M. Pierfitt and J. McCulloch, "Juzzy online: An online toolkit for the design, implementation, execution and sharing of Type-1 and Type-2 fuzzy logic systems," 2014 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2014, pp. 2321-2328
DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2014.6891548.
Project Title: FuzzyR: Fuzzy Logic Toolkit for R
Team Members: Chao Chen, Jon M. Garibaldi, Tajul Razak
Open Source Code URL: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=FuzzyR
Programming Language: R
Type of Software License: GPL-2 | GPL-3
Project Summary:
FuzzyR is a free, open-source fuzzy logic toolbox for the R programming language. Whilst keeping existing functionalities of the previous toolboxes (e.g. FuzzyToolkitUoN), the main extension of the FuzzyR toolbox is the capability to optimise type-1 and interval type-2 fuzzy inference systems based on an extended ANFIS architecture. An accuracy function is also added to provide performance indicators, featuring eight alternative accuracy measures, including a new measure UMBRAE. In addition, graphical user interfaces have been provided so that the properties of a fuzzy inference system can be visualised and manipulated. In the latest release we have made an extension of the toolbox for non-singleton fuzzy logic systems.
References:
C. Chen, T. R. Razak, and J. M. Garibaldi, “FuzzyR: An Extended Fuzzy Logic Toolbox for the R Programming Language,” in Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, pp. 1–8.
C. Chen, Y. Zhao, C. Wagner, D. Pekaslan and J. M. Garibaldi, “An Extension of the FuzzyR Toolbox for Non-Singleton Fuzzy Logic Systems” Accepted to IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, 2021
DOI: 10.1109/FUZZ48607.2020.9177780
Making Visual Analytics an Integral Part of the Technological Infrastructure for Combating COVID-19
Team Members: Min Chen, Rita Borgo, Radu Jianu, Benjamin Bach, Euan Freeman, Hui Fang, Franck Patrick Vidal, Jonathan C. Roberts, Thomas Torsney-Weir, Alfie Abdul-Rahman, Richard Reeve, Louise Matthews, Jason Antony Dykes, Aidan David Slingsby, Daniel William Archambault, Panagiotis Ritsos, Robert S. Laramee, Joseph David Wood, Cagatay Turkay, Kai Xu
Open Source Code URL: https://sites.google.com/view/rampvis/teams
Project Summary:
RAMP VIS is a group of volunteers specialised in Data Visualization and Visual Analytics, who answered a call to support the modelling scientists and epidemiologists in the Scottish COVID-19 Response Consortium (SCRC). Most complex models in the literature take decades and sometimes centuries to develop. Many are built on a substantial amount of post-hoc evidence and analysis, while many are still being improved today. The success can usually be attributed to a collective effort by generations of modelling scientists in data collection, observation, and analysis; hypothesis formulation; and model development, validation, deployment, monitoring, and improvement. In combating COVID-19, such a collective effort in decades has to be compressed into a period of weeks and months.
References:
RAMPVIS: Towards a New Methodology for Developing Visualisation Capabilities for Large-scale Emergency Responses, M. Chen, A. Abdul-Rahman, D. Archambault, J. Dykes, A. Slingsby, P. D. Ritsos, T. Torsney-Weir, C. Turkay, B. Bach, A. Brett, H. Fang, R. Jianu, S. Khan, R. S. Laramee, P. H. Nguyen, R. Reeve, J. C. Roberts, F. Vidal, Q. Wang, J. Wood, K. Xu
ArXiv, 2020, arXiv:2012.04757v1
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments:
RAMP VIS: Making Visual Analytics an Integral Part of the Technological Infrastructure for Combating COVID-19 by Min Chen (Principal Investigator) et al, funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Resource Council (EPSRC EP/V054236/1), UK, 2021, £430,497.00
https://sites.google.com/view/rampvis/
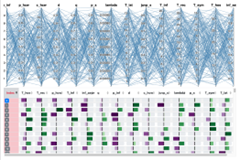
Project Title: Bringing Healthcare Data to Life
Team Members: Qiru Wang, Robert S Laramee, Damon Berridge
Open Source Code URL: https://github.com/thevisgroup/EHealthVis
Project Summary:
This project will develop free, open source, novel visual analytics and visualisation software to study the UK's rapidly increasing volume of big healthcare data. By opening up and exposing the healthcare data analysts to visual and graphical depictions of the enormous collection of the UK's healthcare data including EHR data, a whole new digital world of health understanding, exploration, analysis, comparison and engagement is possible. This healthcare adventure coincides with a rapid rise in interest to improve the collective health of the UK.
References:
Chao Tong, Richard Roberts, Robert S Laramee, Daniel Thayer, Damon Berridge, Cartographic Treemaps for the Visualization of Public Healthcare Data, The Computer Graphics and Visual Computing (CGVC) Conference 2017, 14-15 September 2017, Manchester, UK ( PDF file, supplementary PDF, video, https://doi.org/10.2312/cgvc.20171276 )
Source of Funding/Acknowledgments:
Bringing Healthcare Data to Life by Robert S. Laramee (Principal Investigator), Damon Berridge (Co-Investigator), funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Resource Council (EPSRC EP/S010238/1), UK, 2019-2022, £441,485.97
https://gow.epsrc.ukri.org/NGBOViewGrant.aspx?GrantRef=EP/S010238/1
